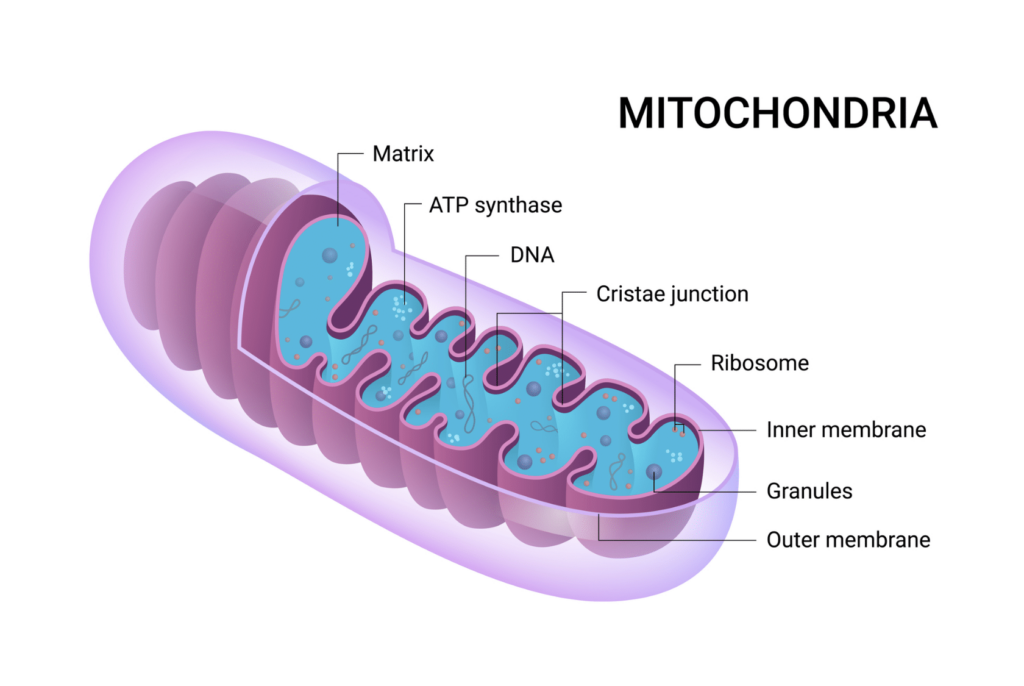
Exercise is an important factor in maintaining overall health and wellness, and it has a number of beneficial effects on the body. One of the key ways that exercise can improve health is by promoting the health of the mitochondria, which are the energy-producing structures within cells.
The Benefits of Exercise on the Mitochondria
The mitochondria are responsible for producing ATP, the body’s main source of energy. They do this through a process called cellular respiration, which involves the breakdown of nutrients such as glucose and fatty acids. Exercise can increase the number and function of mitochondria, leading to improved energy production and increased endurance.
In addition to its effects on energy production, exercise can also have a number of anti-aging effects. As we age, the mitochondria in our cells become less efficient and the production of ATP decreases. This can lead to a decline in physical and cognitive function, as well as an increased risk of age-related diseases.
Anti-Aging Effects of Exercise
Exercise can help to mitigate these age-related changes by increasing the number and function of mitochondria. This can improve energy production, leading to improved physical and cognitive function, as well as a reduced risk of age-related diseases. In addition, exercise can improve cardiovascular health, which is important for maintaining overall health as we age.
Another way that exercise can have anti-aging effects is through its effects on inflammation. Inflammation is a normal immune response that occurs in response to injury or infection. However, chronic inflammation has been linked to a number of age-related diseases, such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s disease. Exercise has been shown to reduce inflammation, which may help to reduce the risk of these age-related diseases.
Exercise and the Brain
Exercise can also have anti-aging effects on the brain. Regular exercise has been shown to improve brain function and protect against age-related cognitive decline. This may be due, in part, to the increased blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain that occurs during exercise. Exercise may also stimulate the production of neurotrophic factors, which are proteins that support the survival and growth of neurons.
In conclusion, exercise has a number of beneficial effects on the body, including the promotion of healthy mitochondria, the reduction of inflammation, and the protection against age-related cognitive decline. These effects can help to improve overall health and wellness, and may also have anti-aging effects. Regular exercise is an important component of a healthy lifestyle, and it is never too late to start reaping the benefits.